 Did you know that 73% of global viewers abandon videos within the first 30 seconds if they can't understand the video? This staggering statistic reveals a critical challenge facing content creators worldwide as they expand into international markets - the subs versus dubs debate.
Did you know that 73% of global viewers abandon videos within the first 30 seconds if they can't understand the video? This staggering statistic reveals a critical challenge facing content creators worldwide as they expand into international markets - the subs versus dubs debate.
The main concern is the costly decision between subtitles and dubbing without clear selection criteria. A comprehensive CSA Research study found that 76% of consumers prefer content in their native language, yet only 23% of businesses have systematic approaches for choosing optimal localization methods. At the same time, AI localization is now reducing costs by up to 71% for subtitling compared to traditional methods (WDHN, 2025). Additionally, subtitles and dubbing offer distinct viewing experiences.
This post aims to alleviate decision paralysis by enabling detailed testing of both approaches. You will learn the exact 7 aspects for choosing between subtitles vs dubbing.
What Are Subtitles and Dubbing
What is Subtitling?
Subtitles are text overlays at the bottom of video content. They only translate the spoken words with the original spoken dialogue and audio information, usually in two types: bilingual subtitles or only subtitles that cover the source language.
They serve multiple purposes: translating foreign language content, providing accessibility for hearing-impaired viewers, and enhancing comprehension in noisy environments.
What is Dubbing?
Dubbing directly replaces the original audio track, with all dialogue spoken by another voice in the target language. It involves transcribing the original text and recording it in the target language.
Dubbing translates the spoken dialogue thoroughly with an immersive audio experience. This process requires careful attention to lip synchronization, matching emotional tone, professional audio mixing, and cultural adaptation. Alternatively, dubbed videos can result in a poor audiovisual experience.
After realizing the main differences between subtitles and dubbing, let’s move to the different methods to decide which one to use for your videos.

Subtitles vs Dubbing: Budget Analysis
Video dubbing can cost 15+ times more than subtitling (Slator, 2024). Different services vary. Here are some examples:
Traditional Subtitles and Dubbing Costs
According to the 2024 Localization World Industry Survey, professional subtitle creation ranges from $1.50-6 per minute of video content. The American Translators Association reports transcription costs of $0.75-2.50/minute, with translation adding $0.08-0.25 per word.
For a 60-minute corporate training video, industry standard pricing ranges from $90-360 based on complexity. CSA Research notes that revision cycles typically add 20-30% to initial estimates.
Professional dubbing costs $100-500 per finished minute, including script adaptation, voice talent, and post-production. SAG-AFTRA rate cards indicate voice talent costs of $200-1,000 per hour for commercial work.
The same 60-minute video could cost $6,000-30,000, depending on language and quality requirements. Slator's industry survey reveals that revision requirements often increase final costs by 40-60%.
Service | Cost Per Minute | 60-Min Video Cost |
|---|---|---|
Subtitles | $1.50 – $6 | $90 – $360 |
Dubbing | $100 – $500 | $6,000 – $30,000 |
AI-Powered Platform Costs
Slator's 2024 AI Translation Report indicates AI-powered localization reduces costs by 60-80% compared to traditional methods. AI dubbing services range from $5-50 per minute based on voice quality and language complexity. This breakthrough makes professional localization accessible to smaller budgets
Take VMEG as an example. Its AI subtitle generation & AI dubbing approximate costs are shown below:Service | Cost Per Minute (Studio Subscription) | 60-Min Video Cost | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
AI Subtitles | $0.667/min | $30 – $120 | ~80%↓ |
AI Dubbing | unlimited dubbing, $10/month with 600 credits, $119.99 billed annually | $600 – $2,400 | ~90%↓ |
Subtitles vs Dubbing: Regional Preference
The regional factor also affects the choice between subtitles and dubbing. Here is some data, showing regional preferences:
Research indicates that over 3 in 4 foreign language viewers prefer content to have subtitles in the United States and the United Kingdom (Statista, 2025). While in Germany, Italy, and France, most viewers (over half) opt for dubbing.
This preference stems from cultural familiarity and a desire to hear original performances. Educational levels and multilingual exposure influence these preferences significantly.
Asian preferences vary dramatically by country and content type, like anime and dramas. Animated videos are popular for dubbing in Japan. But most in Japan and Korea prefer subtitles for other videos. China shows mixed preferences: dubbing for most children's content, subtitles for adult programming.
How to Choose Subtitles vs Dubbing by Content Type
Subtitles dominate content requiring authenticity and user control. Dubbing commands content that needs universal accessibility and immersion, like elementary education or the Dyslexia group.
Content Type Preferences of Subtitles
Art films and documentaries demand subtitles to preserve original voices and cultural context.
Corporate training for reviewing complex concepts through precise subtitles.
75% of students choose subtitles for online courses to master difficult concepts.
Internal communications require instant message consistency.
Social media marketers also prioritize subtitles - subtitles on LinkedIn videos boost business content engagement by 85%.
Budget-sensitive projects prefer subtitles - cost reduction is prioritized.
Content Type Preferences of Dubbing
Choose dubbing for elementary education, dyslexia support, and young audiences to maximize accessibility.
Mainstream theatrical targets reading-averse viewers with audience reach.
Luxury brand campaigns prefer dubbing, forging cultural connections, and emotional marketing.
Age-appropriate comprehension across learning stages in K-12 education.
Animation/kids' content where screen focus is essential uses dubbing.
Subtitles vs Dubbing Timeline Requirements
Traditional Workflow of Subtitles
Subtitles workflow generally contains 4 phases: transcription, translation, timing & formatting, and quality review. The whole process usually takes 3-5 days.
- The original audio is first converted to text, capturing all spoken dialogue, sound effects, and music cues. Ensure accuracy and proper formatting for timing synchronization.
- Native speakers or translators translate the transcribed text frame by frame. Translators adapt cultural references and maintain the original meaning within subtitle constraints.
- Subtitles are synchronized with video timing, ensuring proper display duration and reading comfort. Technical formatting includes positioning, font selection, and file format conversion (SRT, VTT, etc.).
- Final proofreading checks for accuracy, timing issues, and cultural appropriateness. Quality control ensures subtitles meet platform requirements and accessibility standards
Traditional Workflow of Dubbing
Professional dubbing requires 2-4 weeks, including script adaptation, voice casting & recording, audio mixing, and final production.
- The original dialogue is transcribed and translated. Scripts are modified to match mouth movements and maintain natural speech patterns in the target language.
- Voice actors are selected based on character matching, vocal range, and language fluency. Record dialogue in professional studios with director guidance. Multiple takes ensure proper emotion, timing, and synchronization with the original video content.
- Recorded audio is mixed, edited, and synchronized with video. Balance dialogue levels, add effects, and ensure seamless integration with the original soundtrack.
- The complete dubbed version undergoes quality control for sync accuracy and audio quality. Final mastering prepares content for distribution across various platforms and formats.
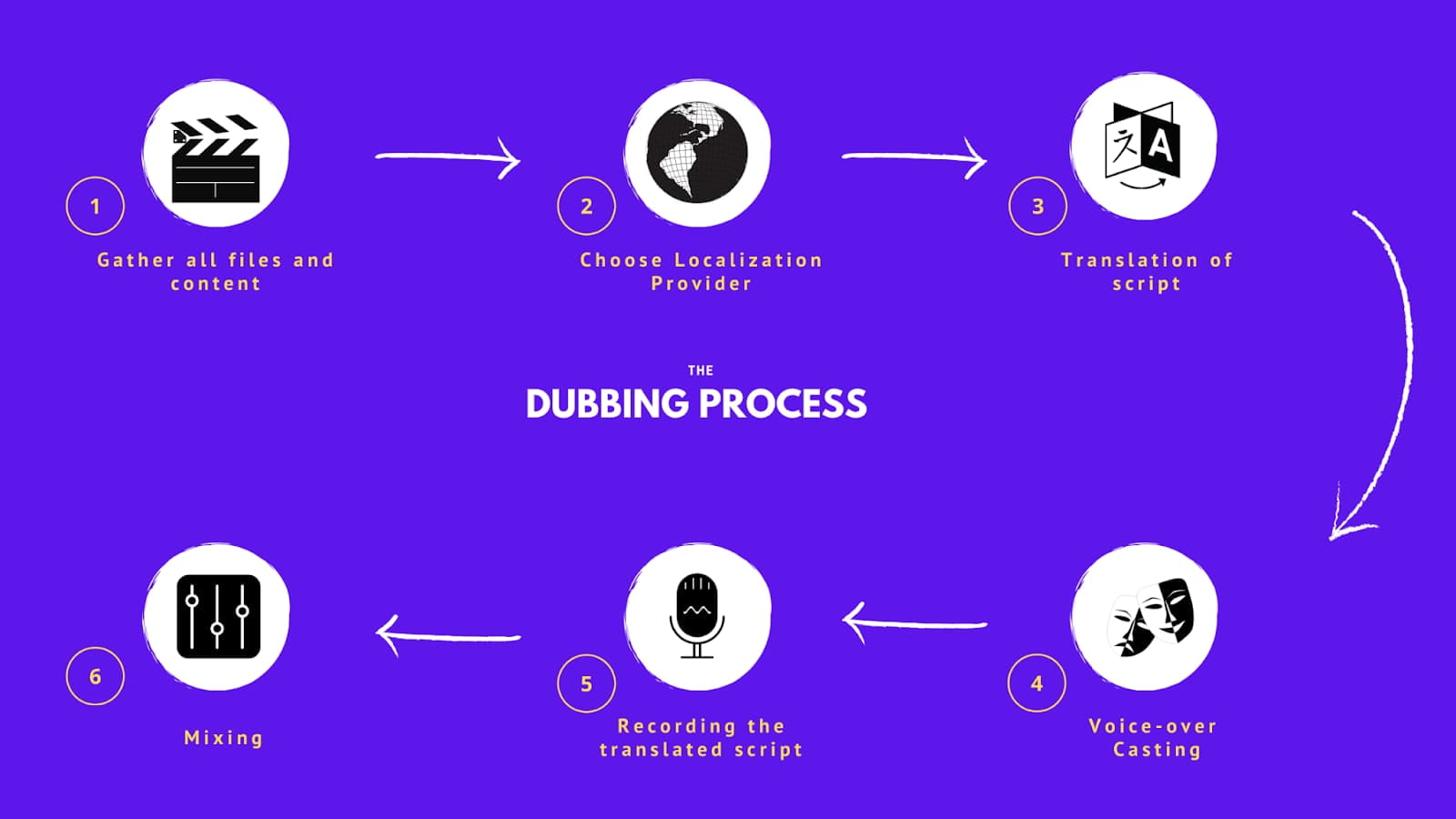
AI-Accelerated Processing of Subtitles vs Dubbing
Generate subtitles with AI in 15-30 minutes. AI automates transcription, translation, and timing synchronization. Quality checks and formatting happen instantly with minimal human oversight required.
While AI dubbing takes 2-4 hours. Voice cloning technology generates target language audio while maintaining original speaker characteristics. Automated lip-sync and audio mixing eliminate traditional production bottlenecks.Subtitles vs Dubbing: Pros & Cons
To balance all preferences, quality, or speed, let’s take an overall look at the benefits and downsides of subtitles and dubbing.
Subtitles Pros & Cons
Preserves Original Performance: Maintains speakers' authentic voices, accents, emotions, and cultural context, especially for drama and documentaries.
Boosts Accessibility: Allows viewers to hear the original delivery while reading the translation, perfect for hearing-impaired audiences.
Enables Cultural Localization: Subtitles are widely used for the translation of any visual text (forced subtitles like street signs, menus, and more) or additional explanations (idioms) in the video.
Cost-Effective & Fast: Generally quicker and cheaper to produce than high-quality dubbing.
Divides Attention: Forces viewers to read while listening, distracting from visual elements.
Accessibility Limitation: Excludes non-readers or those with reading difficulties.
Limited Adaptation: Cannot culturally adapt humor/references as deeply as dubbing.
Dubbing Pros & Cons
Enhances Immersion: Creates a unified viewing experience, allowing full focus on visuals, ideal for mainstream or action content.
Boosts Accessibility: Makes content accessible to young children, low-literacy audiences, and non-readers.
Enables Cultural Localization: Adapts humor, idioms, and references for deeper resonance in target markets.
AI Breakthroughs: Modern AI achieves near-human quality (95%+ accuracy), clones original voices with lip-sync in target language, eliminates speed/quality trade-offs, and automates QA.
Risk of Quality Loss: Poor dubbing can mismatch lip movements, lose emotional tone, causing a bad viewing experience.
Higher Cost & Time: Quality human dubbing is expensive and slow. (Note: AI significantly mitigates this)
Obscures Original Performance: Replaces the original actors' voices.
AI-Powered Subtitles vs Dubbing
Benefits and Challenges of AI Localizations
AI-powered technology eliminates traditional limitations and significant barriers, such as long turnaround times, high costs, limited language support, quality inconsistencies, and extensive human resources. AI localization speeds the process from weeks to hours, costs reduce by 70-90%, and quality remains consistent regardless of project complexity.
Despite advancements, there are still some downsides in context. AI dubbing struggles with emotional depth and natural speech rhythms. Cultural content may be inaccurately localized in subtitling and dubbing. Automation threatens traditional dubbing jobs. Additionally, privacy issues emerge with cloud-based tools.
VMEG AI Localization Platform
VMEG is a professional video localization platform. It processes 2-hour videos in under 20 minutes, regardless of complexity or language combination. This speed enables same-day content localization for time-sensitive campaigns.
Features:
Subtitles Translation & Generation: VMEG enables global market localization across 170+ languages and dialects. Auto-detects speakers + original language in unified workflow.
AI-Powered Voice Cloning: Maintains vocal authenticity for natural-sounding dubbing, with 7000+ voices industry-unique capability.
Pro Accuracy & Sync: 99% accuracy with context-aware translation, including idioms and technical terms.
Automated Lip-sync: Perfect for dubbed content and precise subtitle timing.
End-to-End Format Flexibility: Input your video (MP4/MOV/WEBM) up to 4K/30min/1GB, and quickly output embedded subtitles(SRT/VTT/TXT).
Security & Accessibility: Encrypted processing and exclusive user data access
When to Choose Subtitles and Dubbing?
Choose subtitles when your audience values authenticity (film festivals, documentaries), needs accessibility (hearing-impaired viewers), or prefers reading (higher education, global professionals). Opt for dubbing when targeting young children, low-literacy groups, or regions with strong dubbing traditions, especially for casual viewing environments.
2. Content Type Determines
Subtitles work best for dialogue-heavy content where original voices matter (interviews, dramas) or when visuals require full attention (fast-paced action). Dubbing excels for visual-first content (animation, kids' shows), emotional marketing campaigns, and humor-heavy material needing cultural adaptation.
3. Budgets
Use subtitles for tight budgets, quick turnarounds, or multi-platform distribution (social media, corporate training). Invest in dubbing for premium brand positioning, theatrical releases, or markets where immersion drives engagement.
4. Optimize with Flexibility
Start with low-cost AI solutions to test both methods across audience segments. Scale successful approaches while tracking metrics (completion rates, engagement). Prioritize flexible strategies that adapt to new markets and content volumes using automated localization platforms.
Conclusion
We've explored 7 proven methods from definition to AI-powered subtitles vs dubbing for choosing, including budget, audience preferences, content types, timeline, and more. Each method provides specific angles for optimal decision-making.
The data shows AI-powered solutions like VMEG eliminate traditional trade-offs between cost, speed, and quality in video localization. Modern AI technology achieves professional human quality while reducing costs. Experience the future of video localization with AI-powered subtitle generation and voice cloning dubbing technology that makes global content distribution accessible, affordable, and professional.
Ready to test both subtitles and dubbing approaches for your specific content? Start your free VMEG trial and compare results quickly.
