Dubbed videos are universally accessible with translated dialogue and native-language voices. Dubbing is one of the most effective methods to localize videos.
Maybe you’ve just started localizing videos for new markets, comparing dubbing and subtitling. Or perhaps you're wondering how the voice actors manage to speak perfectly. "What is dubbing?" is the first question to answer.
Maybe you’ve just started localizing videos for new markets, comparing dubbing and subtitling. Or perhaps you're wondering how the voice actors manage to speak perfectly. "What is dubbing?" is the first question to answer.
Here in this post, we will walk you through everything about what dubbing is—from basic definitions to practical tips for dubbing a video or becoming a voice actor. Let's dive in to clearly understand what dubbing is and how to create your own dubbed content easily.
What is Dubbing: The Basics
At its core, dubbing is the post‑production process of replacing the original spoken dialogue in an audiovisual work with a newly translated version.
The dubbing process is widely applied in film, series, animation, game, documentary, marketing video, etc. A dubbed video makes the target audience experience the content as if it were originally produced for them.
The dubbing process is widely applied in film, series, animation, game, documentary, marketing video, etc. A dubbed video makes the target audience experience the content as if it were originally produced for them.

Key Benefits of Dubbing:
- Similar to subtitles, dubbing breaks language barriers with language translation and cultural adaptation, making content understandable to audiences who don't speak the original language. Both can reach a wider audience and markets.
- While dubbing unifies character voices with video subjects to create a higher immersion than reading subtitles, especially for children, the visually impaired, or those who prefer to multitask.
Quick Comparison of Dubbing vs Subtitles vs Voice-over:
Dubbing | Subtitles | Voice-over | |
Key Features | Full replacement for original dialogue, with lip-sync technology or at least timing alignment. | Added text only while keeping the original audio. Cheaper than dubbing. | New audio layered over original. The original is often audible. |
What is the Development of Dubbing
The brief history of dubbing
- Early Talkies (Late 1920s–1930s): With the arrival of sound films, studios scrambled to reach international audiences. Some even re-shot entire movies in multiple languages before true dubbing methods took shape in Europe (France, Germany, Italy, Spain).
- Growing Industry (1930s–1950s): Dubbing became standard practice in Europe, often supported by government policies that promoted domestic language versions.
- Analog Era (1960s–1980s): Advances in magnetic tape and ADR (Automated Dialogue Replacement) made lip-sync more precise. Specialized dubbing studios expanded, and demand surged with the rise of imported animation and foreign TV shows.
- Digital Revolution (1990s–2000s): Digital audio workstations (DAWs), nonlinear editing, and time-coding brought greater accuracy and efficiency. By this stage, localization pipelines had matured, with structured script adaptation and quality checks.
- Streaming Era (2010s): Enter Netflix, Disney+, and global streaming. To serve worldwide audiences quickly, dubbing had to become faster, more scalable, and still maintain quality. This era pushed the industry to work smarter than ever.
- AI Era (2020s–Today): Artificial intelligence is reshaping the field. Tools now automate transcription, translation, voice cloning, cutting costs and timelines dramatically. The future is a hybrid model, blending human creativity with AI-driven speed.
The Different Types of Dubbing
Depending on the different content types and budgets, dubbing has generally been divided into three types below:
- Lip-Sync Dubbing: This is the most common style, typically used for feature films and major TV series. Voice actors speak precisely to match the on-screen actors’ lip movements and emotions, making it look as if the dialogue was originally spoken in the new language.
- Phrase-Sync Dubbing: This approach is often used for documentaries and interviews to narrate or summarize. The original audio is briefly audible before the translated voice-over fades in. The goal isn’t to match every lip movement, but rather to keep the translated speech aligned with the overall pacing and length of the original phrases.
- Time-Sync Dubbing: Common in parts of Eastern Europe, this method uses a single narrator who reads all the translated lines over the existing audio, which remains faintly audible in the background. The narration is timed so it fits naturally with the scene’s rhythm.
Below are some newly named dubbing types, usually clarified into the above main types:
- Animation Dubbing: More flexible because animators (or timing edits) can adapt to new phonemes; focus on performance characterization.
- AI Dubbing: Uses automated transcription, translation, speech synthesis, and voice cloning.
- Simulated Real-Time Dubbing: Emerging for events and streaming; low-latency translation plus synthetic or rapid human re-voicing.
What is the Process of Traditional Dubbing
Professional dubbing is a meticulous, multi-step process that requires a team of skilled specialists.
Step 1. Transcribe and Translate
Translating the script of the video dialogue and narration is the first step. During this process, the translated words need to match the character’s lip movements, timing, and emotions. The goal is to make the audience feel natural, relatable, and culturally relevant.
Step 2. Casting Voice Actors
The voice directors pick voice actors whose voices, ages, and personalities fit the characters. Sometimes they audition for several actors or use voice banks to find the perfect voices that fit both the story and audience expectations.
Step 3. Recording
In the studio, actors watch the scene and record their lines, often using timed cues to hit the right moments. Multiple takes are done to get both perfect timing and authentic emotion, for example, one for lip sync accuracy, another for emotional performance, and sometimes extras as backups.
Step 4. Post-production and Mixing
Finally, the recordings are polished. Editors tweak timing, add breaths or reactions, and adjust the sound so it blends naturally with the music and effects. The result is a seamless, immersive audio track that brings the scene to life.
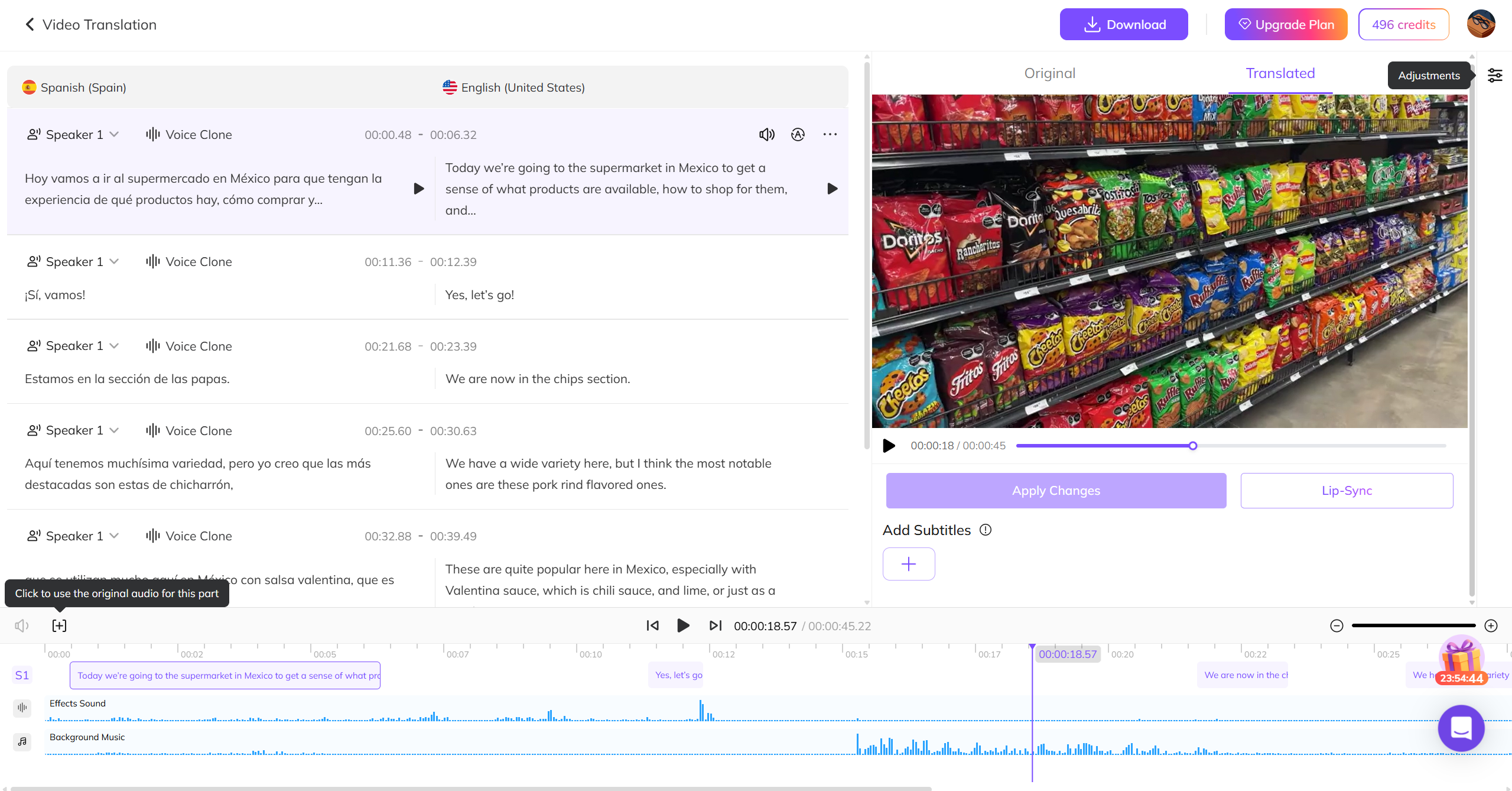
How to Use AI Dubbing Easily with VMEG AI
This part will introduce rapidly developing AI dubbing, which is faster and cost-efficient than the traditional dubbing process with high-accuracy results. For content creators, businesses, and anyone needing a quick turnaround, AI dubbing is worth trying.
Let's see how it works with a tool like VMEG AI, which is a comprehensive video localization platform. It allows you to dub videos with 7000+ natural voices.
Key Features of VMEG AI Dubbing
- Dub Videos in 170+ Languages: Quickly translate and dub your videos into over 170 languages and accents, reaching a global audience in just a few clicks.
- 7,000+ Realistic Voices: Choose from thousands of lifelike AI voices. Adjust pitch, tone, speed, and emotion, or clone voices for consistent brand narration.
- Accurate Lip Sync: AI ensures the dubbed audio matches mouth movements precisely, making videos look natural and professional.
- Editable Subtitles: Generate subtitles automatically and tweak placement for clarity and accessibility.
- Perfect for Content Creators: Localize video content for YouTube, e-learning, marketing, or corporate videos, reaching a wider audience with voice quality.
Simple Dubbing Process with VMEG AI
Step 1: Upload Your Video
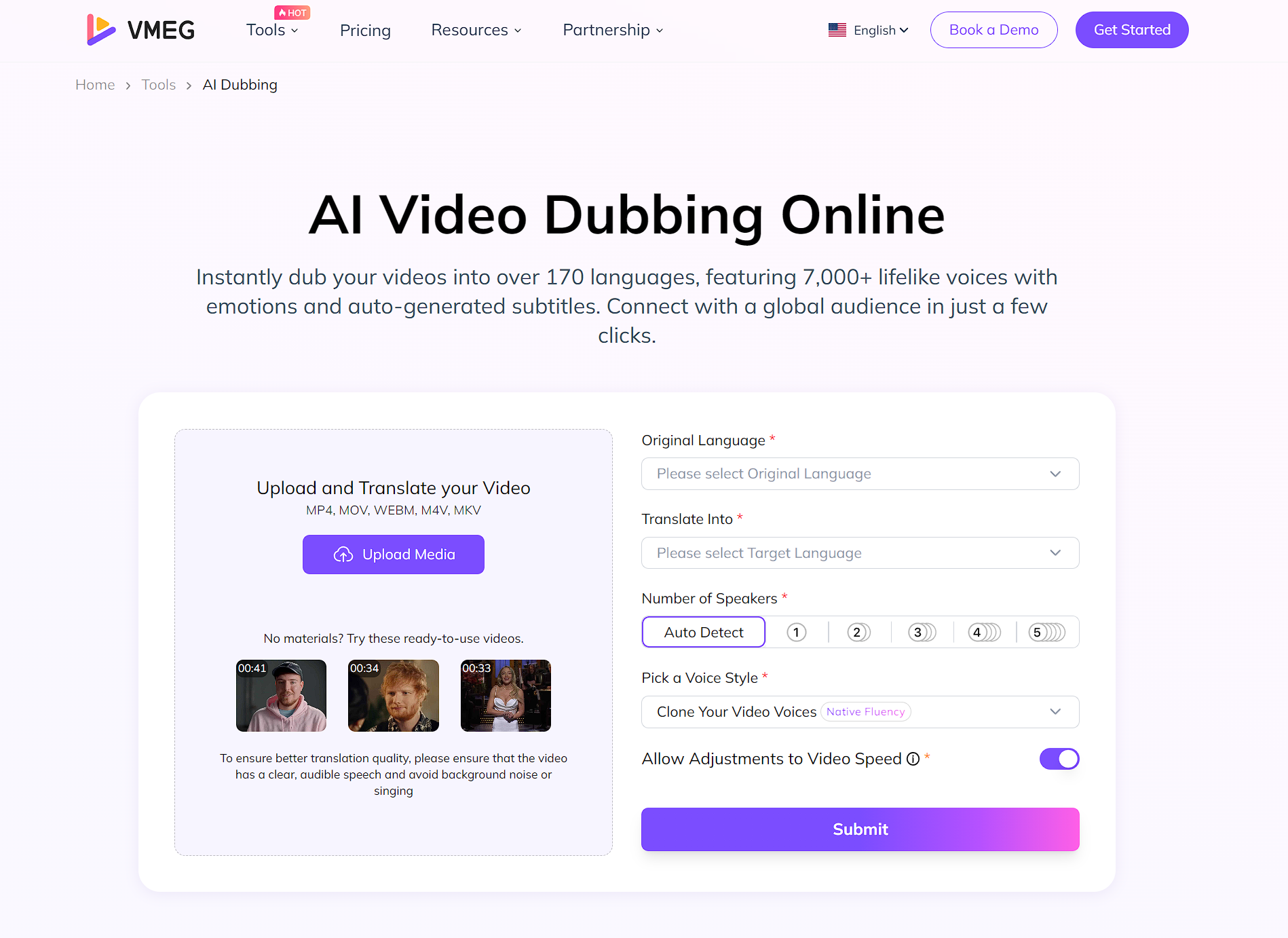
Step 2: Select Dubbing Settings
Select your original and target language, clone your video voices with native fluency or accent, and the platform will instantly transcribe and translate the video.
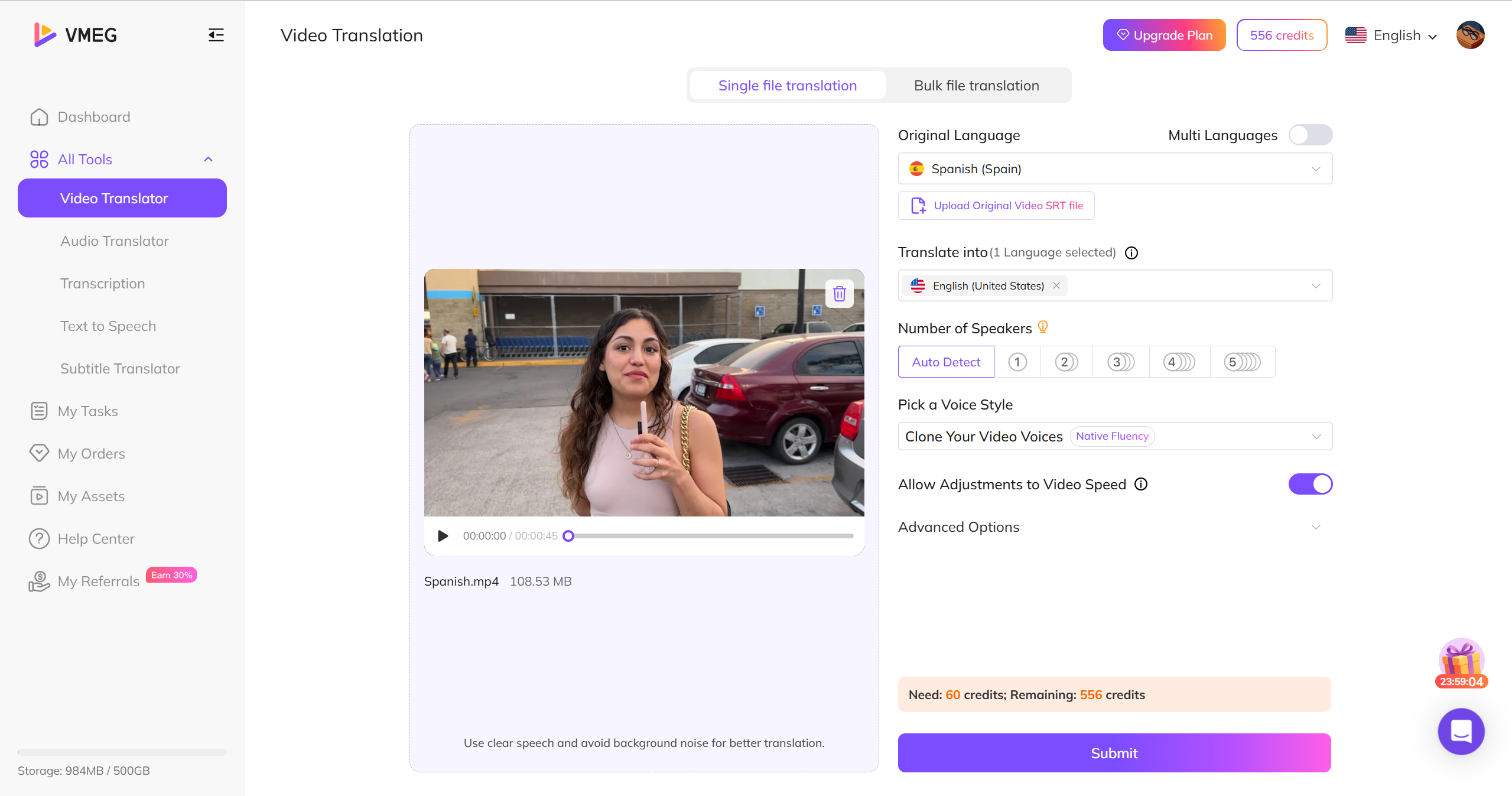
Step 3: Generate and Export
With one click, VMEG generates the dubbed video. You can review and edit the translation for accuracy, listening to dubbing voices while playing. Or add subtitles simultaneously. Click the download button to export your newly dubbed video.
FAQs about What is Dubbing
Dubbing vs. Voice-over
Dubbing replaces the original dialogue completely and syncs with lip movements, while voice-over adds a narrative track over the original audio, often used in documentaries or interviews to explain.
Can AI completely replace human voice actors?
AI can automate many tasks and help to create realistic voices, but human nuance and emotion are still essential for high-quality dubbing, especially for complex characters.
Is dubbing only for movies and TV shows?
No, dubbing is also used in video games, animations, e-learning, advertisements, and more.
Why do some countries prefer dubbing while others prefer subtitles?
Dubbing focuses on immersion with natural and native-language experience, while subtitles preserve the original audio track to maintain cultural and language accessibility.
Dubbing or subtitles preferences are largely a matter of historical tradition, economic, and cultural preferences.
Dubbing or subtitles preferences are largely a matter of historical tradition, economic, and cultural preferences.
How to become a voice actor
To start a career in dubbing as a voice actor, focus on training your voice first. Create a demo reel to present your works, and seek opportunities through casting platforms, agencies, or freelance sites.
Finally, build your network for knowing dubbing better and keep improving through practice, workshops, and industry connections.
Finally, build your network for knowing dubbing better and keep improving through practice, workshops, and industry connections.
Conclusion
Dubbing is a historical and effective way of breaking language barriers. It makes video stories accessible for audiences everywhere. Whether you’re a content creator looking to reach new markets, a film lover curious about the process, or an aspiring voice actor ready to dive in, dubbing offers endless opportunities.
Now that we have entered the AI dubbing era, dubbing is much easier for anyone. Try an AI tool like VMEG AI to localize your videos, reaching a wider audience and achieving your goals.
